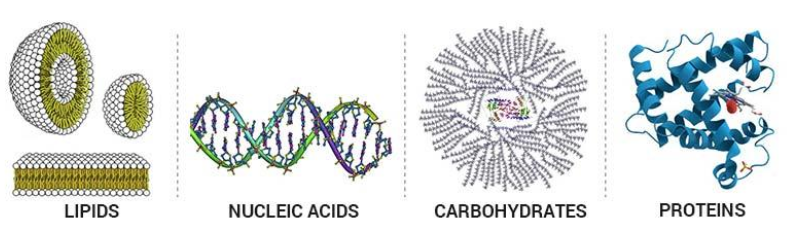
Biomolecules
Biomolecules include both micromolecules, e.g. amino acids, nitrogenous bases, fatty acids, sugar, etc. and macromolecules, such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.
Living organisms are made up of organic as well as inorganic substances. For analysing the organic constituents of living tissue, we mix it with CCl3COOH (Trichloroacetic acid) and make a slurry by grinding. We get two fractions:
Acid soluble fraction- Organic micromolecules (biomolecules) (mol wt. 18-800 Da) and inorganic compounds, e.g. phosphate, sulphate, etc. It mostly accounts for the cytoplasm
Acid insoluble fraction- Polymeric macromolecules (mol wt. >10 thousand Da) and also lipid (a component of the cell membrane and form water-insoluble vesicles on fragmentation)
The inorganic constituents can be estimated by analysing the ash formed after burning a tissue completely.
All the macromolecules are homo or heteropolymers of various simple compounds.
- Protein- Polymer of amino acids
- Carbohydrates (Polysaccharides)- Polymer of simple sugars, e.g. glucose, fructose
- Fats- Fatty acids and glycerol
- Nucleic acids- Nitrogenous bases, sugar and phosphate
- Water constitutes 70-90% of cells. Proteins are 10-15%, nucleic acids are 5-7%, carbohydrates are 3%, lipids are 2% and the rest 1% are ions.
- Amino acids, fatty acids, sugars, etc. are called primary metabolites, which take part in the physiological processes. Other than these, there are varied compounds present in the cells of plants, microbes and fungi, which are called secondary metabolites. Some of the secondary metabolites have ecological significance.
- Secondary metabolites can be grouped under various categories:
- Pigments (anthocyanins, carotene, etc.), drugs (curcumin, vinblastine, etc.), gum, rubber, toxins (ricin, abrin), alkaloids (codeine, morphine), essential oils, terpenoids, lectins (concanavalin A), etc.

Comments
Post a Comment