Endometriosis
Endometriosis
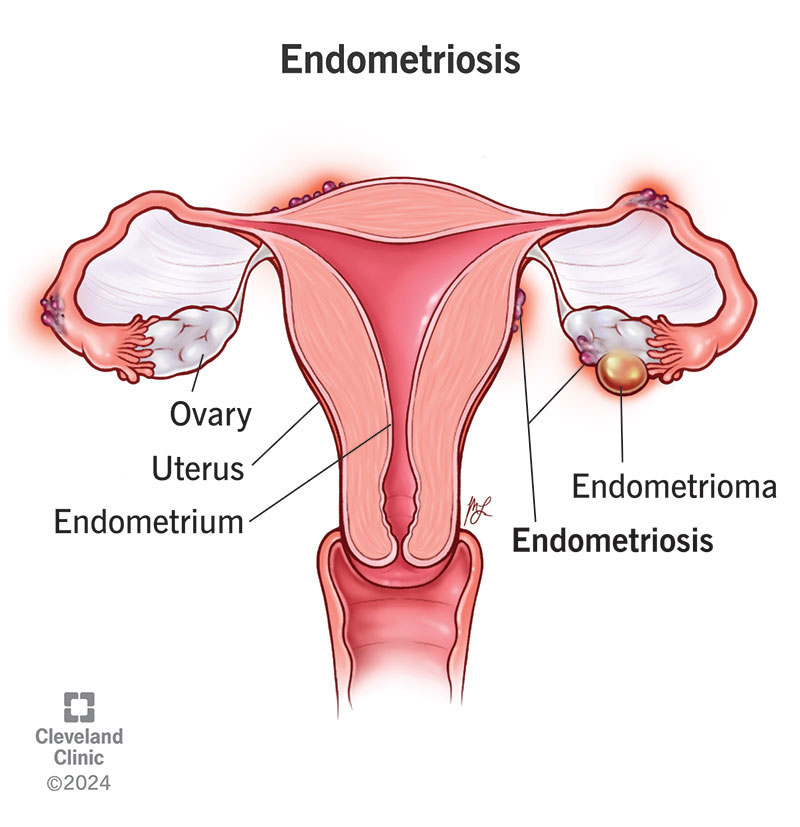
Endometriosis is a chronic condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, often affecting the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and pelvic tissue. This can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications.
Symptoms
- Pelvic Pain: Often the most common symptom, especially during menstruation.
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: Increased bleeding during periods or bleeding between periods.
- Pain During Intercourse: Discomfort or pain during or after sex.
- Pain with Bowel Movements or Urination: Typically observed during menstruation.
- Infertility: Many women with endometriosis face challenges when trying to conceive.
- Other Symptoms: Fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and nausea, especially during menstrual periods.
Causes
The exact cause of endometriosis is not fully understood, but several theories exist:
- Retrograde Menstruation: Menstrual blood flows backward through the fallopian tubes into the pelvic cavity instead of leaving the body.
- Embryonic Cell Transformation: Hormones such as estrogen may transform embryonic cells into endometrial-like cell implants during puberty.
- Surgical Scars: Previous surgeries, like hysterectomy, may allow endometrial cells to attach to surgical wounds.
- Immune System Disorders: Issues with the immune system may make the body unable to recognize endometrial-like tissue growing outside the uterus.
Diagnosis
- Pelvic Exam: A healthcare provider may manually check for abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or MRI can help identify cysts associated with endometriosis.
- Laparoscopy: A surgical procedure that allows direct visualization of endometrial tissue outside the uterus.
Treatment
Treatment options can vary based on the severity of symptoms and whether a woman wishes to become pregnant:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen).
- Hormonal Therapies: Birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or other hormonal medications can help regulate or stop menstruation, reducing pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical removal of endometriosis implants or even a hysterectomy may be considered.
- Fertility Treatments: If infertility is a concern, assisted reproductive technologies like IVF may be suggested.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats may help manage symptoms.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can alleviate some symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels.

Comments
Post a Comment