Genetic Disorders diseases
Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders are diseases caused by abnormalities in an individual's DNA, which can occur due to mutations in single genes, changes in chromosome structure or number, or complex interactions between genes and the environment.
Types of Genetic Disorders
Single-Gene Disorders:
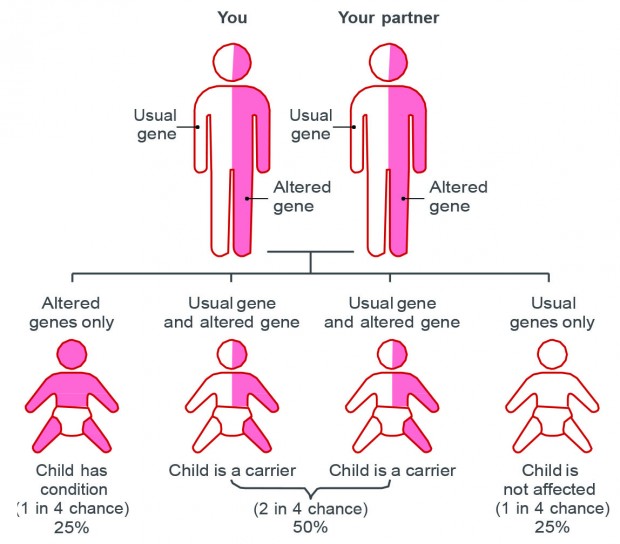
- Description: Caused by mutations in a single gene.
- Examples:
- Cystic Fibrosis: Affects the respiratory and digestive systems.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: A blood disorder caused by a mutation in the hemoglobin gene.
- Huntington's Disease: A neurodegenerative disorder resulting from a mutation in the HTT gene.
Chromosomal Disorders:
- Description: Caused by abnormalities in chromosome number or structure.
- Examples:
- Down Syndrome: Caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21).
- Turner Syndrome: A condition in females characterized by the absence of one X chromosome.
- Klinefelter Syndrome: Affects males who have an extra X chromosome (XXY).
Multifactorial Disorders:
- Description: Result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Examples:
- Heart Disease: Influenced by genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors.
- Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes has both genetic and environmental components.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Risk is influenced by genetic factors, age, and lifestyle.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Symptoms: Vary widely depending on the disorder but can include physical abnormalities, developmental delays, chronic illnesses, or increased susceptibility to diseases.
- Diagnosis:
- Genetic Testing: Analyzing DNA to identify mutations associated with specific genetic disorders.
- Blood Tests: Screening for metabolic or genetic conditions.
- Imaging Studies: May be used to identify structural abnormalities.
Treatment Options
- Management: Many genetic disorders have no cure but can be managed through various treatments, including:
- Medications: To manage symptoms or prevent complications.
- Therapies: Such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy.
- Surgery: May be needed for certain conditions or to correct physical abnormalities.
- Gene Therapy: An emerging treatment that aims to correct defective genes.
Prevention and Genetic Counseling
- Genetic Counseling: Provides information and support to individuals and families about genetic disorders, including risks, testing, and family planning.
- Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD): Used in conjunction with IVF to screen embryos for specific genetic disorders before implantation.

Comments
Post a Comment