Marine biochemistry
Marine biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes and substances that occur in marine organisms and ecosystems. This field is crucial for understanding the biochemical mechanisms that drive life in ocean environments and how these processes impact the broader marine ecosystem.
Marine Biochemistry
Metabolism of Marine Organisms:
- Examining how marine organisms, from phytoplankton to fish, metabolize nutrients and energy.
- Understanding adaptations to varying environmental conditions, such as pressure, temperature, and salinity.
Biochemical Cycles:
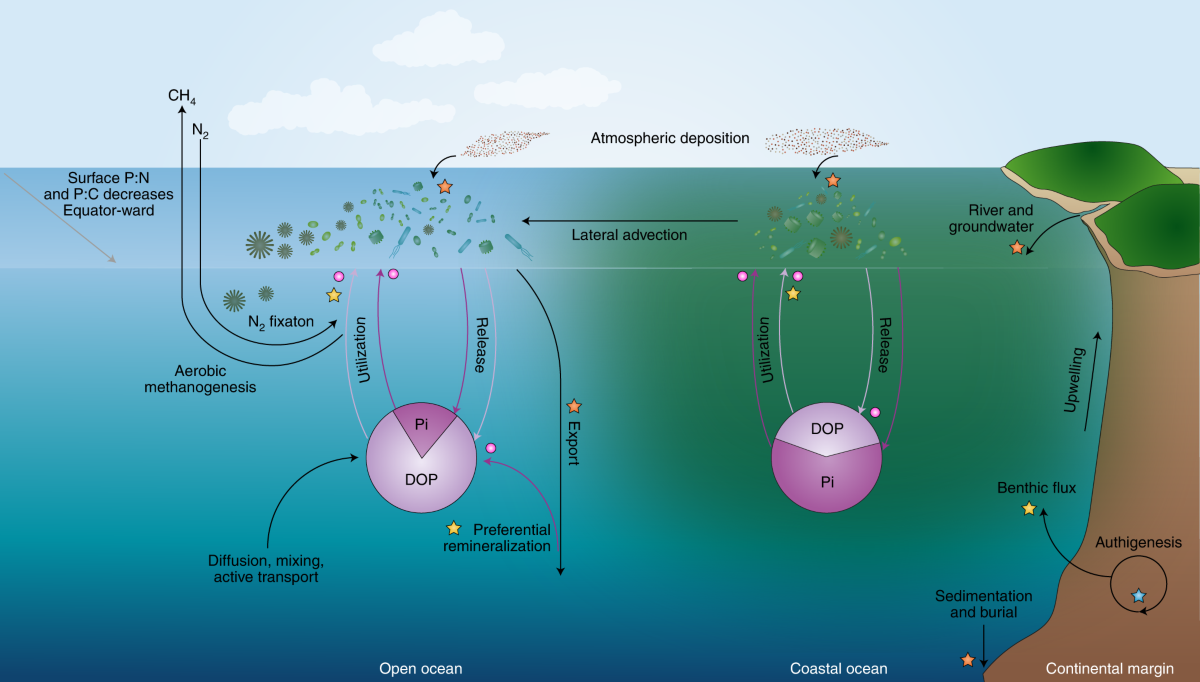
- Investigating cycles like the nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus cycles in marine environments.
- Studying how these cycles are influenced by biological activity and human impacts.
Marine Toxins:
- Analyzing the production of toxins by marine organisms, such as algae (e.g., harmful algal blooms) and certain fish.
- Understanding the biochemical pathways involved in toxin synthesis and their effects on marine food webs and human health.
Biotechnology Applications:
- Exploring potential biotechnological applications of marine organisms, including drug discovery, bioremediation, and biofuels.
- Investigating enzymes and compounds from marine organisms for industrial applications.
Climate Change Impact:
- Studying how changes in ocean chemistry (like acidification) affect marine life at the biochemical level.
- Understanding the implications for marine food webs and global carbon cycling.
Photosynthesis and Primary Production:
- Investigating the biochemistry of photosynthetic organisms in the ocean, such as phytoplankton, and their role in carbon fixation and oxygen production.
Marine Lipids and Nutritional Biochemistry:
- Studying the role of lipids in marine organisms, including omega-3 fatty acids, and their nutritional benefits for human health.
Importance
Marine biochemistry provides insights into:
- Ecosystem Functioning: Understanding the biochemical processes that sustain marine ecosystems.
- Sustainable Practices: Informing conservation efforts and sustainable management of marine resources.
- Human Health: Identifying marine-derived compounds for potential pharmaceutical applications.
Conclusion
The field of marine biochemistry is essential for understanding the complex interactions within marine ecosystems and the implications of environmental changes. Ongoing research continues to uncover the vast biochemical diversity of marine life and its significance for both ecology and human benefit.

Comments
Post a Comment